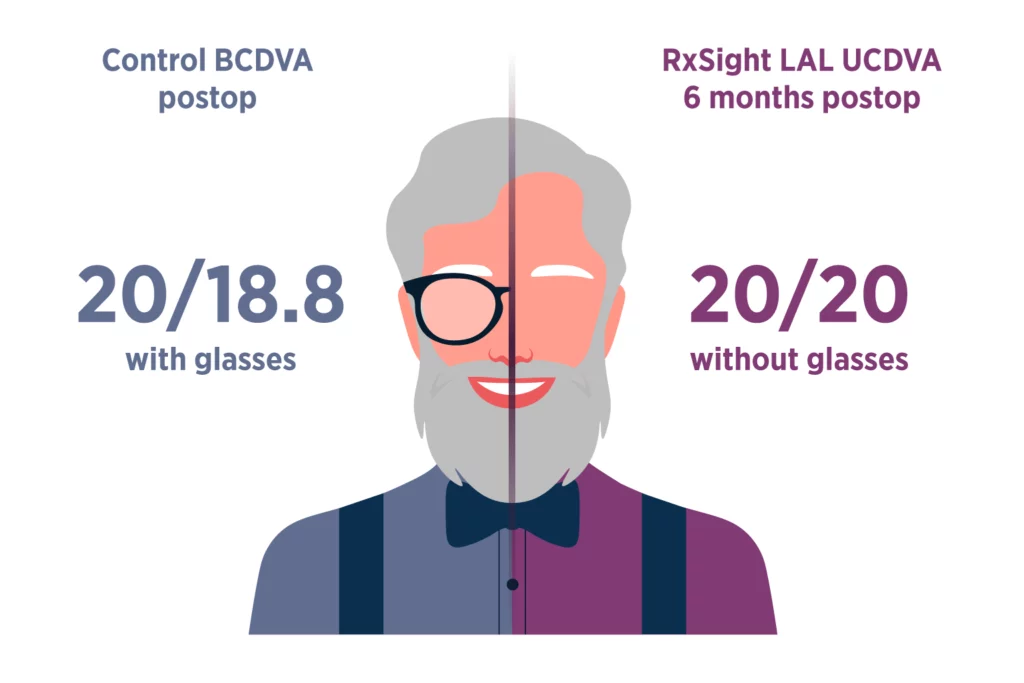
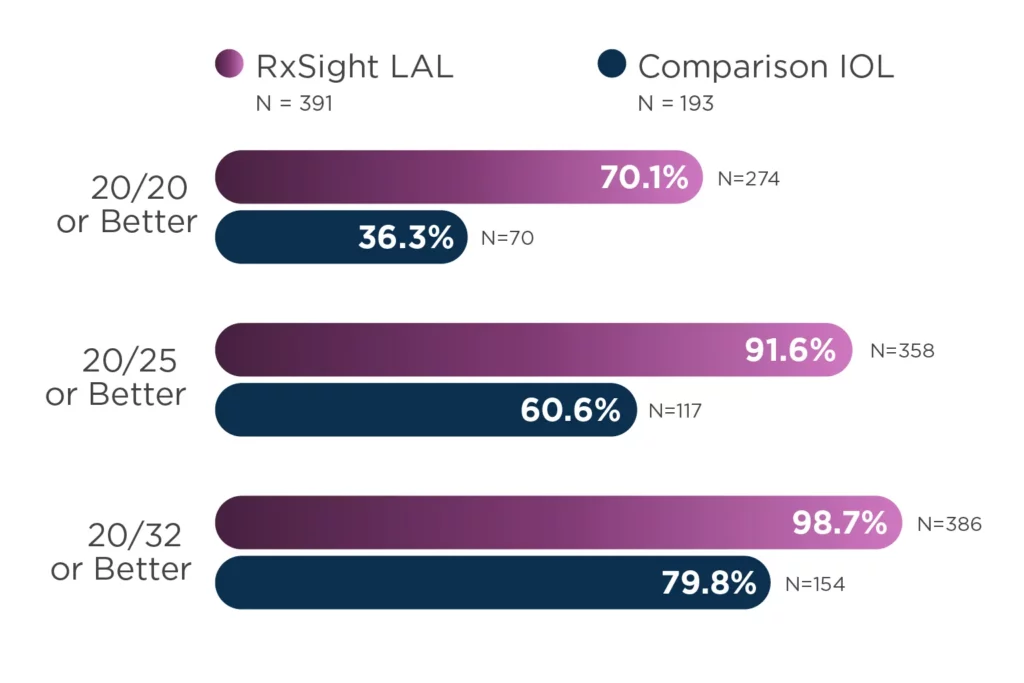
Light Adjustable Lens™ (LAL™)
Indications
The Light Adjustable Lens and Light Delivery Device™ (LDD™) system is indicated for the reduction of residual astigmatism to improve uncorrected visual acuity after removal of the cataractous natural lens by phacoemulsification and implantation of the intraocular lens in the capsular bag in adult patients with preexisting corneal astigmatism of ≥ 0.75 diopters and without preexisting macular disease. The system also reduces the likelihood of clinically significant residual spherical refractive errors.
Contraindications
The Light Adjustable Lens is contraindicated in patients who are taking systemic medication that may increase sensitivity to ultraviolet (UV) light as the LDD treatment may lead to irreversible phototoxic damage to the eye; patients who are taking a systemic medication that is considered toxic to the retina (e.g., tamoxifen) as they may be at increased risk of retinal damage during LDD treatment; patients with a history of ocular herpes simplex virus due to the potential for reactivation from exposure to UV light; patients with nystagmus as they may not be able to maintain steady fixation during LDD treatment; and patients who are unwilling to comply with the postoperative regimen for adjustment and lock-in treatments and wearing of UV protective eyewear.
Warnings
Careful preoperative evaluation and sound clinical judgment should be used by the surgeon to decide the risk/benefit ratio before implanting an IOL in a patient with any of the conditions described in the Light Adjustable Lens and LDD Professional Use Information document. Caution should be used in patients with eyes unable to dilate to a pupil diameter of ≥ 7 mm to ensure that the edge of the Light Adjustable Lens can be visualized during LDD light treatments; patients who the doctor believes will be unable to maintain steady fixation that is necessary for centration of the LDD light treatment; patients with sufficiently dense cataracts that preclude examination of the macula as patients with preexisting macular disease may be at increased risk for macular disease progression; and patients at high risk for future vitreoretinal disease that may require silicone oil as part of therapy. The Light Adjustable Lens must be implanted in the correct orientation with the back layer facing posteriorly.
Precautions
The long-term effect on vision due to exposure to UV light that causes erythropsia (after LDD treatment) has not been determined. The implanted Light Adjustable Lens MUST undergo a minimum of 2 LDD treatments (1 adjustment procedure plus 1 lock-in treatment) beginning at least 17-21 days post-implantation. All clinical study outcomes were obtained using LDD power adjustments targeted to emmetropia post LDD treatments. The safety and performance of targeting to myopic or hyperopic outcomes have not been evaluated. The safety and effectiveness of the Light Adjustable Lens and LDD have not been substantiated in patients with preexisting ocular conditions and intraoperative complications. Patients must be instructed to wear the RxSight-specified UV protective eyewear during all waking hours after Light Adjustable Lens implantation until 24 hours post final lock-in treatment. Unprotected exposure to UV light during this period can result in unpredictable changes to the Light Adjustable Lens, causing aberrated optics and blurred vision, which might necessitate explantation of the Light Adjustable Lens.
Adverse Events
The most common adverse events (AEs) reported in the randomized pivotal trial included cystoid macular edema (3 eyes, 0.7%), hypopyon (1 eye, 0.2%), and endophthalmitis (1 eye, 0.2%). The rates of AEs did not exceed the rates in the ISO historical control except for the category of secondary surgical interventions (SSI); 1.7% of eyes (7/410) in the Light Adjustable Lens group had an SSI (p < .05). AEs related to the UV light from the LDD include phototoxic retinal damage causing temporary loss of best spectacle corrected visual acuity (1 eye, 0.2%), persistent induced tritan color vision anomaly (2 eyes, 0.5%), persistent induced erythropsia (1 eye, 0.3%), reactivation of ocular herpes simplex Infection (1 eye, 0.3%), and persistent unanticipated significant increase in manifest refraction error (≥ 1.0 D cylinder or MRSE) (5 eyes, 1.3%).
Caution
Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Please see the Professional Use Information document for a complete list of contraindications, warnings, precautions, and adverse events.
Light Adjustable Lens+™ (LAL+®)
Indications
The Light Adjustable Lens+ (LAL+) and Light Delivery Device™ (LDD™) system is indicated for the reduction of residual astigmatism to improve uncorrected visual acuity after removal of the cataractous natural lens by phacoemulsification and primary implantation of the intraocular lens in the capsular bag in adult patients with preexisting corneal astigmatism of ≥ 0.75 diopters and without preexisting macular disease. The system also reduces the likelihood of clinically significant residual spherical refractive errors.
Contraindications
The LAL+ is contraindicated in patients who are taking systemic medication that may increase sensitivity to ultraviolet (UV) light as the LDD treatment may lead to irreversible phototoxic damage to the eye; patients who are taking a systemic medication that is considered toxic to the retina (e.g., tamoxifen) as they may be at increased risk of retinal damage during LDD treatment; patients with a history of ocular herpes simplex virus due to the potential for reactivation from exposure to UV light; patients with nystagmus as they may not be able to maintain steady fixation during LDD treatment; and patients who are unwilling to comply with the postoperative regimen for adjustment and lock-in treatments and wearing of UV protective eyewear.
Warnings
Careful preoperative evaluation and sound clinical judgment should be used by the surgeon to decide the risk/benefit ratio before implanting an IOL in a patient with any of the conditions described in the LAL+ and LDD Professional Use Information document. Caution should be used in patients with eyes unable to dilate to a pupil diameter of ≥ 7 mm to ensure that the edge of the LAL+ can be visualized during LDD light treatments; patients who the doctor believes will be unable to maintain steady fixation that is necessary for centration of the LDD light treatment; patients with sufficiently dense cataracts that preclude examination of the macula as patients with preexisting macular disease may be at increased risk for macular disease progression; and patients at high risk for future vitreoretinal disease that may require silicone oil as part of therapy. The LAL+ must be implanted in the correct orientation with the back layer facing posteriorly.
Precautions
The safety and effectiveness of the LAL+ has not been substantiated in clinical trials. The effects of the LAL+ optical design on the quality of vision, contrast sensitivity, and subjective visual disturbances (glare, halo, etc.) have not been evaluated clinically. Surgeons must weigh the potential benefits of the modified optical design of the LAL+ against the potential for risks associated with degradation in vision quality and the lack of clinical data to characterize the impact of the LAL+ optical design on contrast sensitivity and subjective visual disturbance. These considerations may be especially relevant to patients with certain pre-existing ocular conditions (prior corneal refractive surgery, irregular corneal astigmatism, severe corneal dystrophy, macular disease, or optic nerve atrophy, etc.) or intraoperative conditions (posterior capsular rupture, complications in which the IOL stability could be compromised, inability to place IOL in capsular bag, etc.). The long-term effect on vision due to exposure to UV light that causes erythropsia (after LDD treatment) has not been determined. The implanted LAL+ MUST undergo a minimum of 2 LDD treatments (1 adjustment procedure plus 1 lock-in treatment) beginning at least 17-21 days post-implantation. All clinical study outcomes were obtained using LDD power adjustments targeted to emmetropia post-LDD treatments. The safety and performance of targeting to myopic or hyperopic outcomes have not been evaluated. The safety and effectiveness of the LAL+ and LDD have not been substantiated in patients with preexisting ocular conditions and intraoperative complications. Patients must be instructed to wear the RxSight-specified UV protective eyewear during all waking hours after LAL+ implantation until 24 hours post final lock-in treatment. Unprotected exposure to UV light during this period can result in unpredictable changes to the LAL+, causing aberrated optics and blurred vision, which might necessitate explantation of the LAL+. When performing refraction in patients implanted with the LAL+, confirmation of refraction with maximum plus manifest refraction technique is recommended.
Adverse Events
The most common adverse events (AEs) reported in the randomized pivotal trial of the parent LAL included cystoid macular edema (3 eyes, 0.7%), hypopyon (1 eye, 0.2%), and endophthalmitis (1 eye, 0.2%). The rates of AEs did not exceed the rates in the ISO historical control except for the category of secondary surgical interventions (SSI); 1.7% of eyes (7/410) in the LAL group had an SSI (p < .05). AEs related to the UV light from the LDD include phototoxic retinal damage causing temporary loss of best spectacle corrected visual acuity (1 eye, 0.2%), persistent induced tritan color vision anomaly (2 eyes, 0.5%), persistent induced erythropsia (1 eye, 0.3%), reactivation of ocular herpes simplex Infection (1 eye, 0.3%), and persistent unanticipated significant increase in manifest refraction error (≥ 1.0 D cylinder or MRSE) (5 eyes, 1.3%).
Caution
Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Please see the Professional Use Information document for a complete list of contraindications, warnings, precautions, and adverse events.